| CS631p - Human-Computer
Interaction |
| Spring 2001 |
| Lecture 5 |
Development Tools
What are Development
tools? :
Tools that help a developer convert interface specifications
into an interactive system and that support all phases of system refinement
including prototypes, implementation, testing, maintenance, and enhancement
Conventional
Development Tools
-
Window Systems
-
Constrain each application or application component to a
particular frame on the screen (the window)
-
Provide an:
-
Input model - user interaction sent to application as events
-
Graphic model - output graphics
-
Window management - window opened and closed, resized, moved,
and iconified
-
Presentation stype enforecement - e.g. X, Mac, Win95, Win3.1
e.g. X Windows:
-
Network-based - uses client-server architecture -Any Xapp,
called a client, runs on any machine on the net
-
Server process, which resides on workstation, mediates all
usr input and display output
-
Server translates person's input into X events and sends
to appropriate client
-
Client interprets events and sends graphics direct to server
on how to update display
-
Special client, called Window Manager, is responsible for
overall look and feel
BUT:
-
Windowing systems provide too low-level an abstraction for
building an application
-
Better - have toolkits, interface builders, user interface
mgmt. Systems.
Toolkits - a variety of interface building blocks
called widgets and language for putting together
e.g. Motif, Xview, Tk/Tcl
-
Widgets - buttons, menus, sliders, scrollbars, text
editors, canvases for graphics, terminal windows
-
Interfaces are built by using widgets, and programming languages
(e.g Tk/Tcl)
-
Widget Limitations:
-
Widget sets are small and restrict interaction techniques
-
Widgets are good for creating control panels BUT poor for
what is seen inside. (e.g. Tk/Tcl for visualization resorts to OpenGL
for graphics)
-
Programming in an abstract language is not easy way for putting
widgets together.
Motif Examples: (from: http://www.cm.cf.ac.uk/Dave/X_lecture/X_book_caller/index.html
)
(Common Desktop Environment
(CDE))
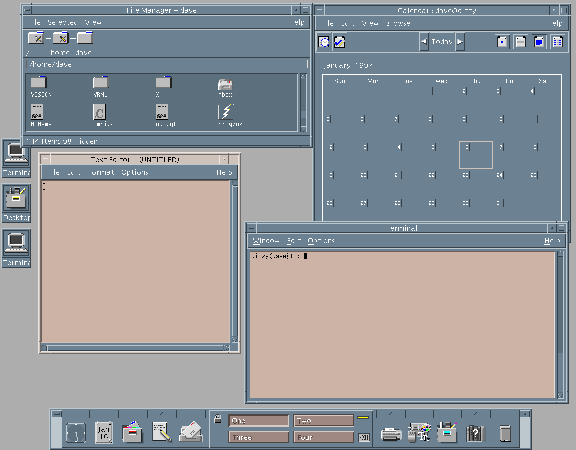
Front Panel
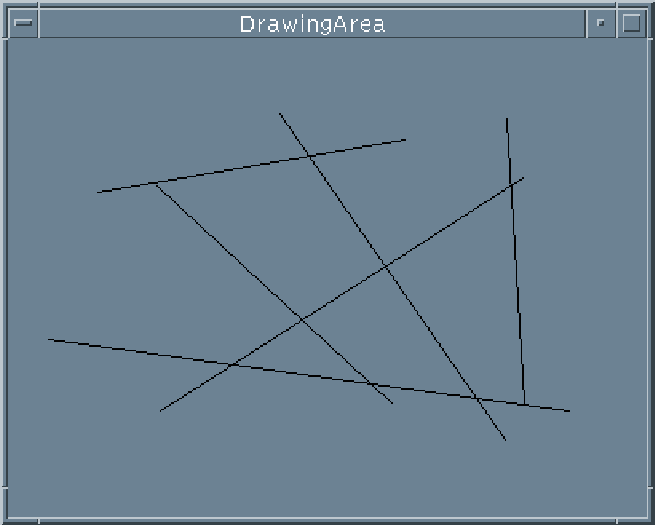
Drawing Widget
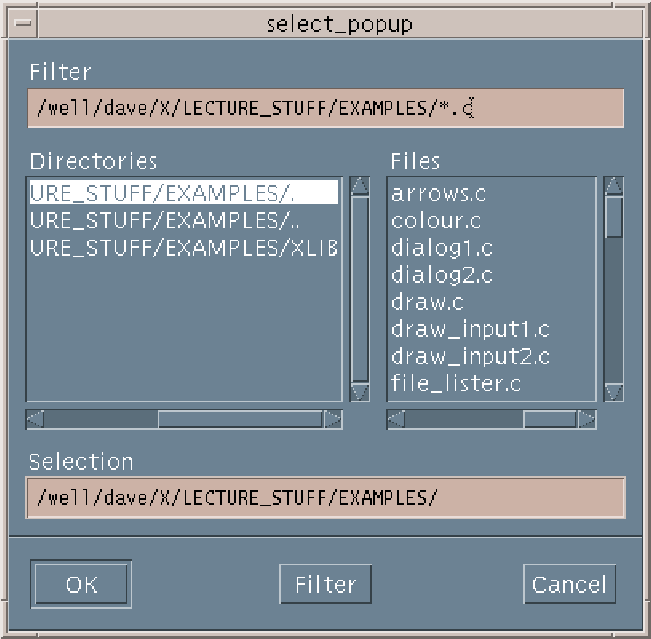
File Selection Box Widget
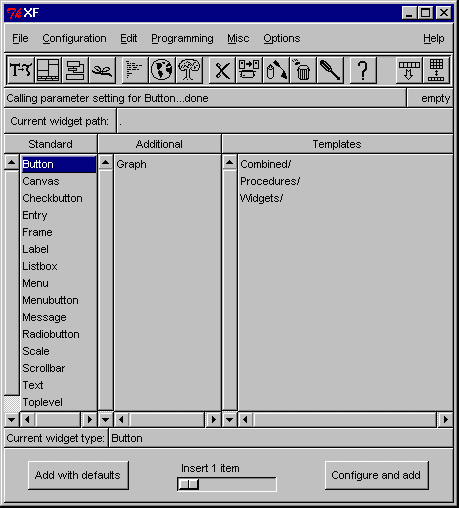
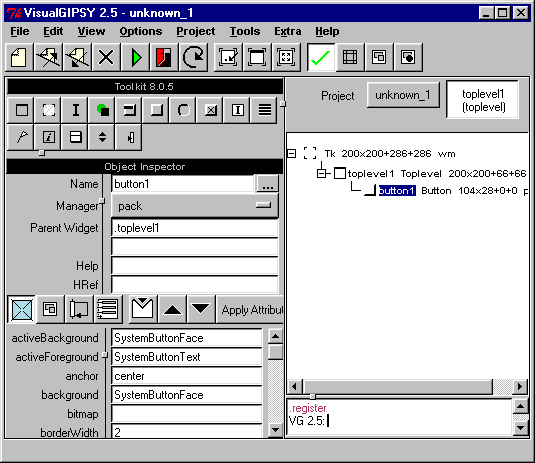
Interactive Builders - provide a direct manipulation
of graphical and interface toolkits. Some are integrated into toolkit environment,
e.g.
-
Implementer selects a widget from a palette, places it on
the screen, sets its attributes through form filling, or direct manipulation.
Links made as callbacks that are written as procedures.
-
Allows developers to test interfaces as they are being constructed.
-
Also can build interface prototypes with Macromedia Director
and HyperCard
Examples:
User Interface Management Systems (UIMS) - better
said as "user interface development environments."
Separate Applications into 3 modules:
-
Presentation Graphics - output to screen.
-
Dialog Control - how input is passed to Applications
-
Application Interface - how interface hooks into application
code
Good - Application and Interface separated
Bad - Hard for designer to separate two in practice
e.g. SUIT:
Can learn to build an interface in a few hours.
Designed for teaching.
Adv:
-
Portability across platforms
-
Standard widget set
-
Runs applications plus application builder
-
Allows for custom widgets
Novel Approaches
to Developer tools
Garnet - System
and Tools - comprehensive toolkit:
-
Easy manipulation of graphical objects and behavior
-
Can create and edit application specific graphical objects
and predefined widgets
-
All objects are defined in Opal graphical toolkit
-
Opal implemented atop KR - prototype instance object oriented
system
-
If prototype is edited - all objects changed
-
Constraints
-
Constrain-based tooled that allows developer to specify relationships
among components (therefore at runtime system makes sure changes in one
object are made in others)
-
Interactors
-
Separate look from feel allows many different styles of menus.
-
Programming by demonstration (PBD)
-
Examples of the interface are created and then the program
is generated.
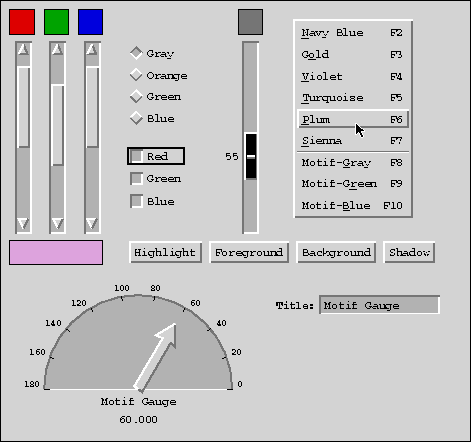
Sample Applications of Garnet:
http://www.cs.cmu.edu/afs/cs/project/garnet/www/screen-shots/screen-shots.html
Amulet - Garnet's
Successor
http://www.cs.cmu.edu/afs/cs/project/amulet/www/amulet-home.html
User interface development environment for C++ and is
portable across X11 on all kinds of Unix (Sun, Dec, HP, SGI, Linux, NetBSD,
etc.), Microsoft Windows 95 and NT, and the Macintosh.
-
Amulet helps create graphical, interactive user interfaces.
-
Amulet includes features designed to make creation of highly-interactive,
graphical, direct manipulation user interfaces significantly easier employing:
-
prototype-instance object model
-
constraints
-
high-level input handling including automatic undo
-
built-in support for animation
-
gesture-recognition
-
full set of widgets.
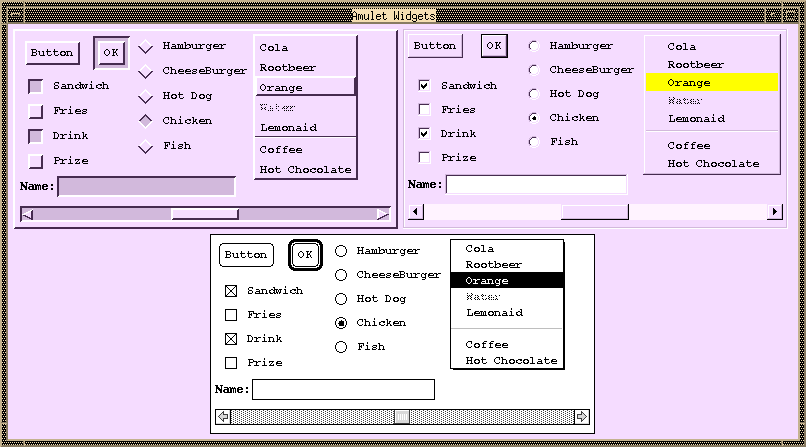
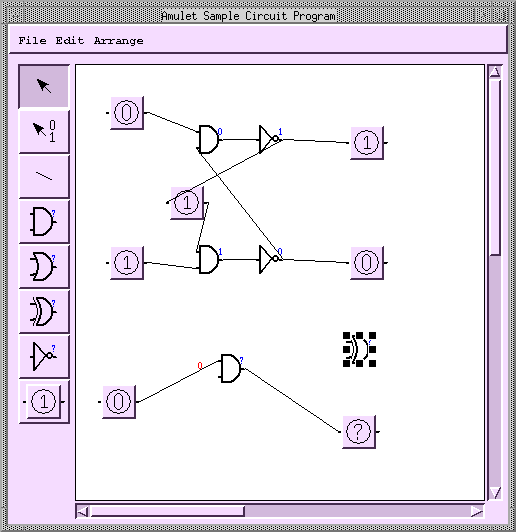
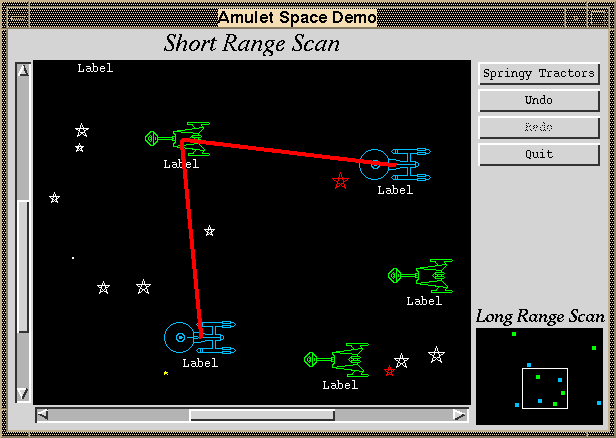
Tools for Entire
Development Cycle
-
Toolkits should support (and supported by UIMs):
-
Interface specification
-
Implementation
-
Testing
Alternate Approach - instead of "artifact centered"
of existing tools USE "semantically driven user interface design."
Semantic model - interface developed as a declarative
description and model becomes a plan that is used to let the developer
manipulate in a way that is appropriate to its stage in the lifecycle.
e.g. IBM's Interactive Transaction System (ITS)
-
Action layer - implements semantics of application
functions independent of interface.
-
Dialog layer - interface is a set of logica; frames
containing objects that define flow of control between frames and actions.
-
Style rules - defines the presentation and behavior
of interactive widgets.
-
Style programs - implement actual widgets.
NOTE: Each layer corresponds to work roles of the development
team members:
-
Application programmer - works with action layer
-
Application expert - composes dialog rules
-
Style programmers - build style programs
-
Graphic designers - compose style rules
Groupware Toolkits
Supports and augments group work where conventional toolkits
do not work
e.g. Groupkit Project - University of Calgary
http://www.cpsc.ucalgary.ca/projects/grouplab/groupkit/
-
Used to build real-time applications such as drawing tools,
editors and meeting tools that are shared simultaneously among several
users.
-
Used for prototyping groupware, investigating multi-user
architectures and interfaces, and as a CSCW teaching tool.
Example:
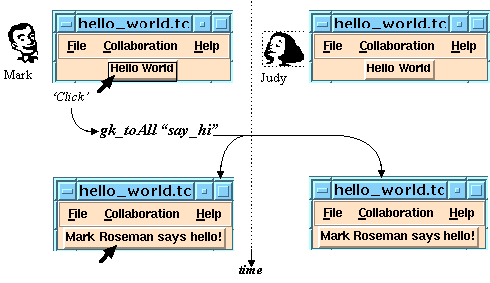
-
Diagram at right and code below fully define a "Hello World"
program written in GroupKit.
-
When one person presses the hello button, all people in the
conference see that person say hello!
1.gk_initConf $argv
2.gk_defaultMenu .menubar
3.pack .menubar -side top -fill
x
4.set greetings "[users local.username]
says
hello!"
5.button .hello -text "Hello
World" \
-command "gk_toAll
say_hi
\"$greetings\""
6.pack .hello -side top
7.proc say_hi {new_label} {
8. .hello configure -text $new_label
9. after 2000 {.hello configure
-text "Hello World"}
10.}
Example:
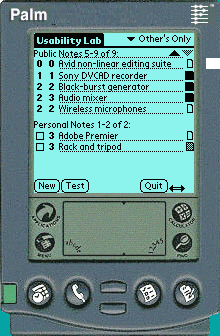
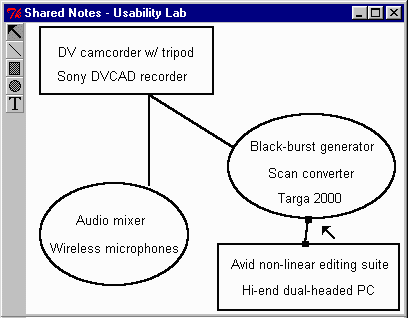
SharedNotes is a system that allows people to create and
manipulate both personal and public notes between three devices: a personal
digital, assistant (PDAs, in this case the Palm Pilot), a large public
display, and their office computer (which acts both as a personal device
and a system for remote collaboration).
-
The left figure shows how a person would see their personal
and public information on their PDA, while the right figure shows how this
same information is reflected in the public display.
-
Essentially, people can work on their PDAs or computers for
personal work, bring some or all of their work into a meeting using a public
display, work on the public display either directly or indirectly through
their PDAs, and walk away with a record of all public contributions.