|
Lecture
2 - Computer Hardware and Software |
Video Display Devices
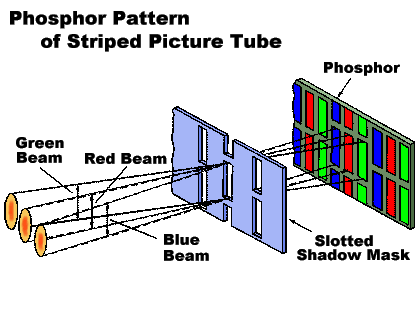
Cathode Ray Tube (CRT)
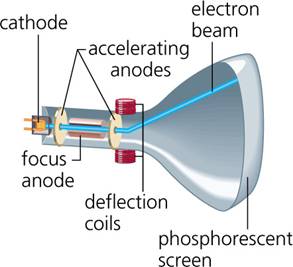
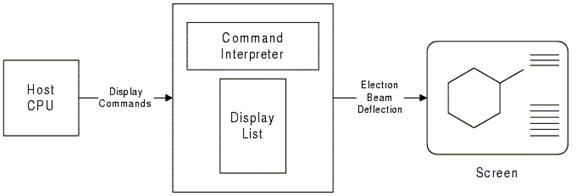
Vector Display
Random Scan display
Calligraphic Refresh Display
Direct-view Storage Tube Display
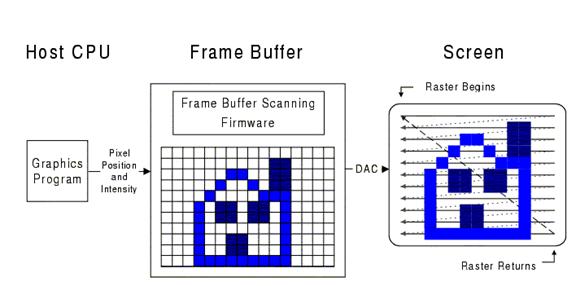
Raster Display
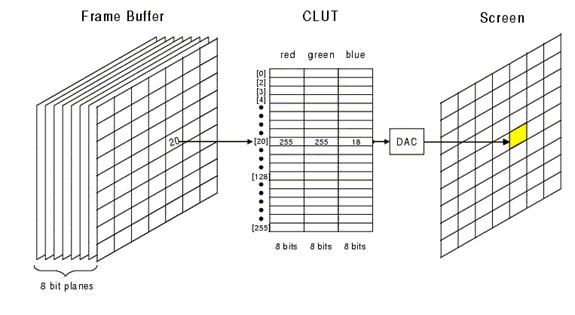
CLUT
Flat Panel Displays
Emissive:
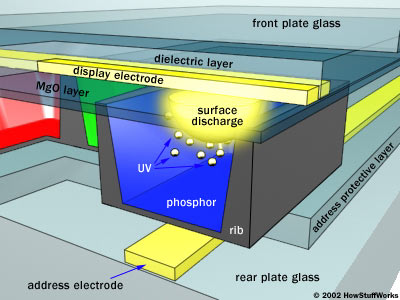
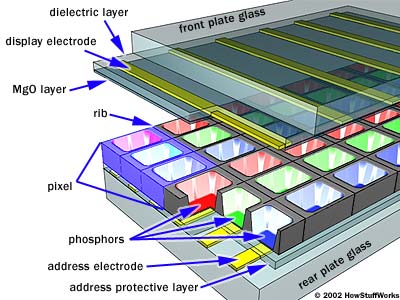
Plasma
Each pixel made of three cells containing xenon and neon gas
Horizontal and vertical electrodes create unique grid to locate cell positions
Gas in each cell is ionized when a voltage difference is applied to intersecting electrodes
The current creates a rapid flow of charged particles, which stimulates the gas atoms to release photons of ultraviolet light
Photons excite the phosphor coated on the inside wall of the cell.
(Pictures from: "How Plasma Displays Work")
Non-emissive:
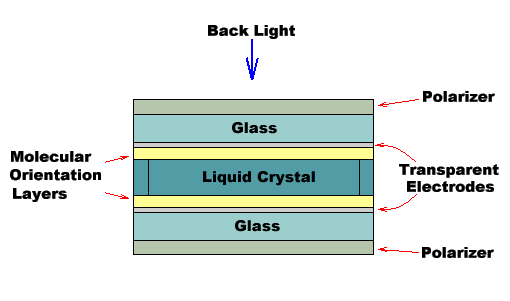
LCDs\
Organic molecules that align themselves in crystalline structures in the absence of external forces
Application of external force rearranges them as if they were a liquid
Liquid
crystals respond to heat or electromagnetic forces
LCDs used as optical modulators
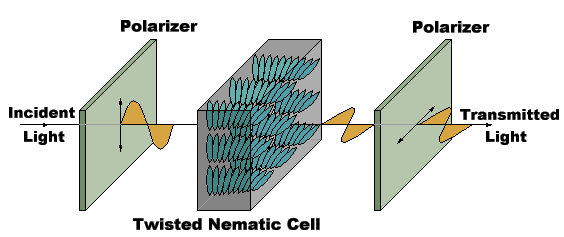
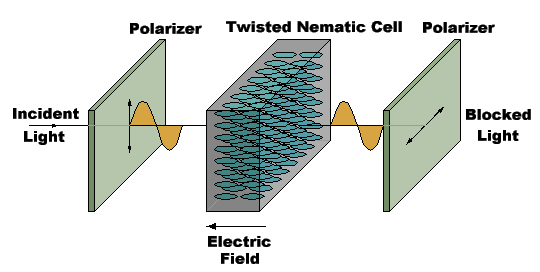
Change polarization
In unexcited or crystalline state, LCDs rotate the polarization of light by 90 degrees.
In the presence of an electric field, LCDs behave like a liquid and align their electrostatic charges with E field.
Augmented Display Systems
Virtual Reality
Definition - VR is a computer generated, interactive, three-dimensional environment in which a person is immersed.
- This implies:
- Requires a high performance computer graphics system to provide an adequate level of realism.
- The virtual world is interactive. A user requires real-time response from the system to be able to interact with it in an effective manner.
- The last point is that the user is immersed in this virtual environment. This usually means that the user wears a head mounted display.
Virtual Reality Interface Devices
HMD - head mounted display
- Best known approach to VR
- Coupled with head tracking
- Stereo binocular view of the virtual world often with stereo audio
- By virtue of tracking the viewing position (the head) and orientation in the physical world, the view and perspective of the virtual are consistent with what one would experience in the physical world from the same actions.
- Permit some means of input, such as a dataglove or some other high degree of freedom input to support interaction with the displayed virtual world.
- stereo display, much like a pair of glasses that provides a view into the virtual world.
- The physical form of these “glasses” can range from something on the scale of a motorcycle helmet to a pair of sunglasses
- Great variety in display quality
- Goal is to provide the widest field of view at the highest quality and with the least weight and at a reasonable cost.
- Issues:
- HMDs cover eyes
- Virtual world seen at the expense of the physical.
- Users cannot directly see:
- their hands or the devices that they are controlling
- objects or other people who are in their immediate physical environment
- Solution:
- Some representation of physical world entities must appear in the virtual
- Mount one or more video cameras onto the HMD and feed the signals to the displays

Surround Environments
Cave based VR
- User functions within a room on which one or more of the surfaces (walls, floor, ceiling …) is the display
- Some or all of the walls of a room are rear-projection stereo displays
- User wears glasses to enable viewing of stereo images
- Since glasses are transparent, one can see the physical as well as the virtual world
- Computer generated objects appear to enter into the physical space of the Cave itself, where the user can interact with them directly
- User’s head position is tracked within the Cave so that what is displayed preserves proper perspective, etc., in adapting to movements and change of location of gaze
- Issue:
- Two people in cave - both are viewing the same displays, preventing each from own “point of view.”
- Both viewers look at different things and different directions, but do so as if from the perspective of the current location of the head tracker.
- Some mechanism for interacting with what is scene.
1992/93 - EVL's
Cave (http://www.evl.uic.edu/home.html
)
Cruz-Neira, Sandin, DeFanti, Kenyon and Hart
Electronic Visualization Lab -
- Generic Immersive VR Environment
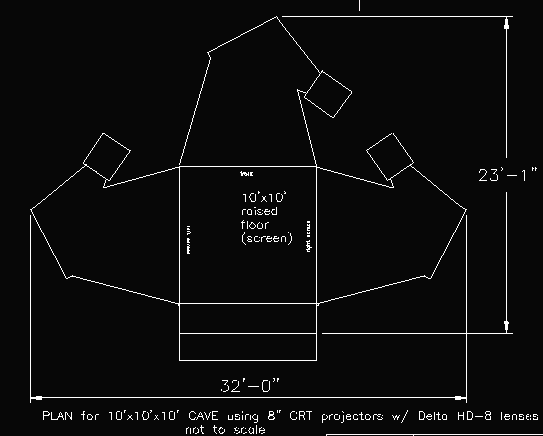
- A theater 10x10x9 feet, made up of three rear-projected screens for walls and a reflective projection for the floor.
- High resolution, high bandwidth, short persistance CRT projectors throw full-color workstation fields (1024x768 stereo) onto the screens, giving approximately 3,000 linear pixel resolution to the surrounding composite image.
- Computer-controlled audio provides a sonification capability to multiple speakers.
- User's head and hand orientation and position are aquired using an Ascension tracking system with tethered electromagnetic sensors.
- Stereographics' LCD stereo shutter glasses are used to separate the alternate fields going to the eyes.
- SGI InfiniteReality Engine is used to create the imagery that is projected onto the walls and floor.




Trimension
Cabin - Fully enclosed cave
Image Construction : 5 - 6 Cameras

Domes and Walls
SkyVision Full-Dome (SkySkan.com)
- Sloping seats, zenith position.
- Different projector orientations .

Imax
- Primary goal is to fill peripheral vision.
- 16:9 aspect ratio format
Personal Domes


Elumens Visionstation (VS) - Hemispherical Display
Elumens Visionstation (VS3)
Elumens Visionstation (VS3)
Depth: 8'-10" (106")
Height: 7'-9" (93")
Width: 11'-4" (136")
Partial Immersion
Panoramic - Curved Walls
- Typically use RGB projectors (Varing focal depth)
- Edge blending (On computer or with video hardware)
- Small "sweet" spot.


Trimension (others - Barco)
MultiWalls
- How to synchronise multiple devices (Computer, DVD)
- Multiple pipe graphics cards (Cost)
- Seams between walls (Aligned, edge blending)
- Front vs back projection (Space)


Three Wall - CAEV -
Tables, Desks, Single Screens
Immersadesk 2 - EVL


Fakespace
Trimension
The Grip Project - UNC
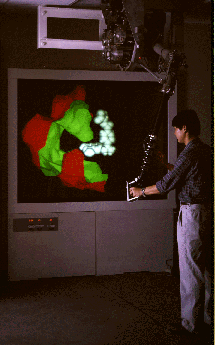
The NanoManipulator - UNC Chapel
Hill
http://www.cs.unc.edu/Research/nano/
Movie
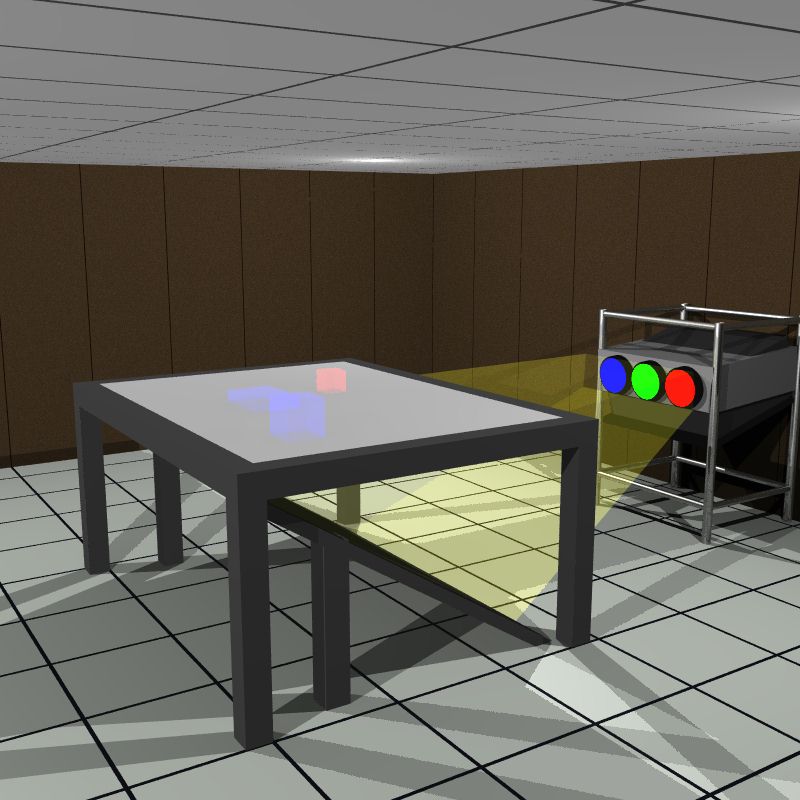
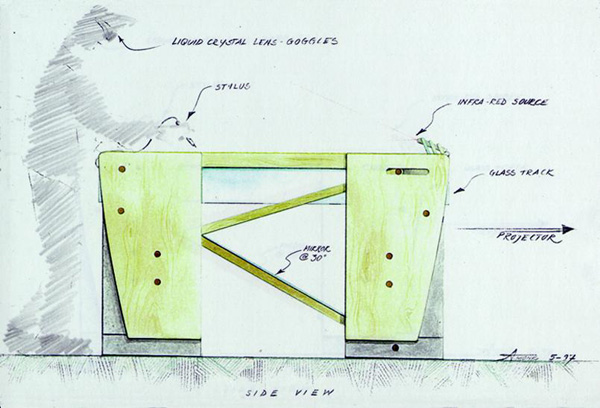
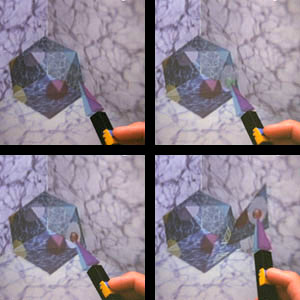
Responsive Workbench - 1993
- 3D interactive workspace originally developed by Wolfgang Krueger at GMD
- Computer-generated stereoscopic images are projected onto a horizontal tabletop display surface via a projector-and-mirrors system, and viewed through shutter glasses to generate the 3D effect
- A 6DOF tracking system tracks the user's head, so that the user sees the virtual environment from the correct point of view.
- A pair of gloves and a stylus, also tracked by the system, can be used to interact with objects in the tabletop environment.

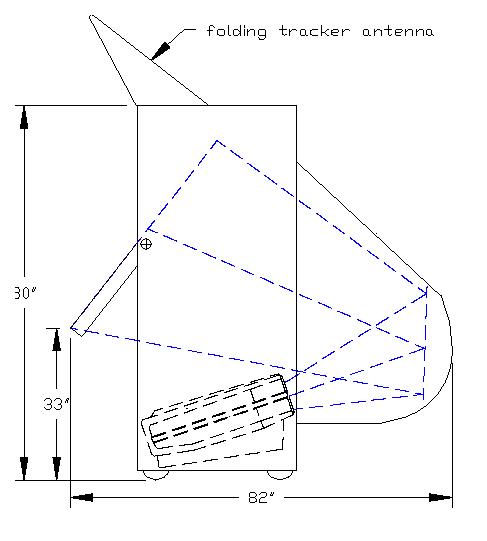
Low Cost Stereo Table - Pace University CAM )

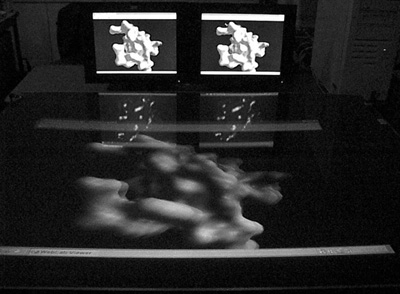
Cubby -



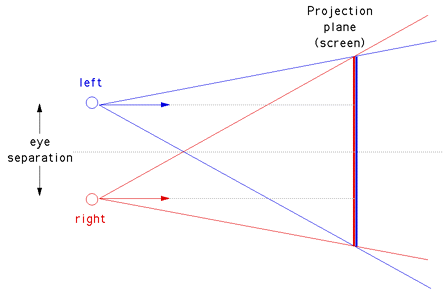
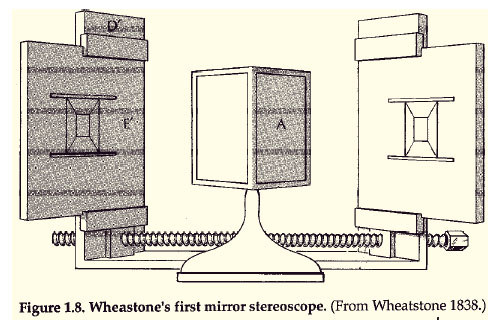
Stereoscopic Displays
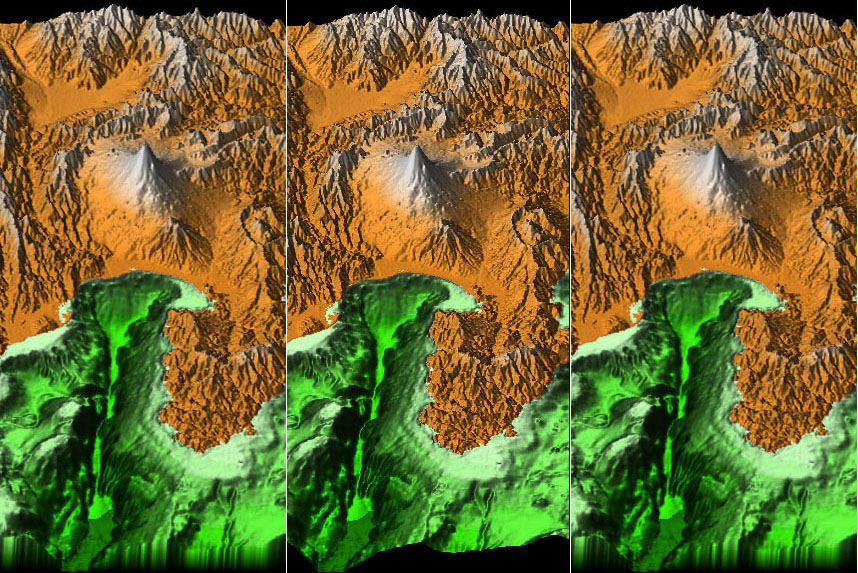
Mount Fuji Stereo Pairs
Free Viewing
Cross Eyed Viewing
Left Eye
Right eye
Left Eye
- Head Mounted Displays

5DT HMD 800
Display Resolution: 800x600x3(rgb)
pixels - Full SVGA
Optics Field of View: 28 (H)
x 21 (V) degrees
Headphones:
Type: Sennheiser HD 25 closed
dynamic headphones
Frequency Responce: 16Hz -
22Hz (3dB)
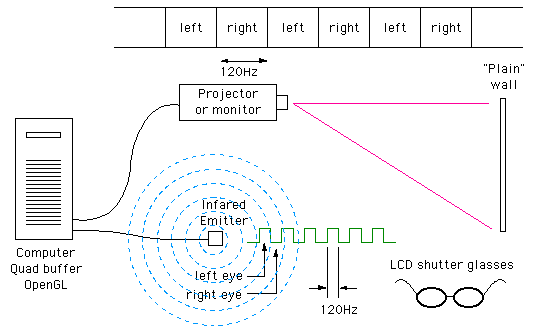
- Shutter Glasses (Active Stereo)


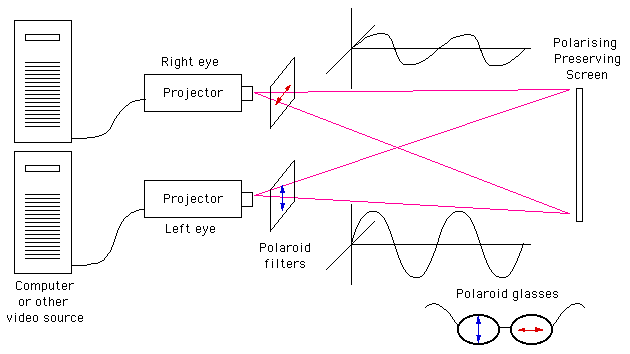
- Polarized Glasses (Passive Stereo)
Autostereographic Display

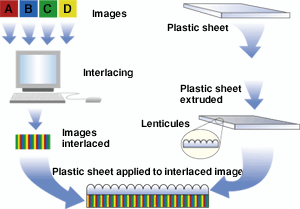
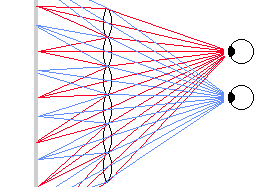

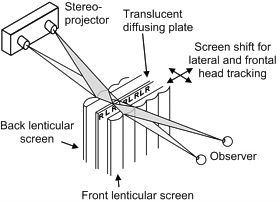
MultiMo3D , Heinrich-Hertz-Institut für Nachrichtentechnik,
Principles and prototype of a 50-inch projection-type dual lenticular screen
3D display.
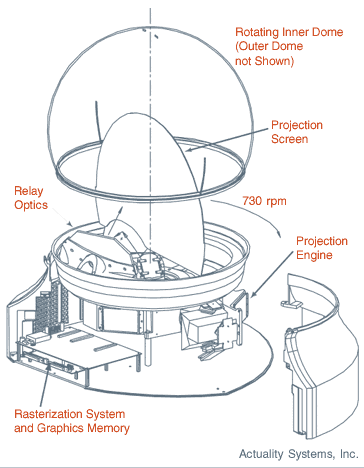
Volumetric Display - Actuality Systems
Image Size and Display Type
- Approx.
10" diameter spherical image
- Swept-screen multiplanar volumetric display
- Autostereoscopic: no viewing goggles
- Volume-filling imagery
- Supports many simultaneous viewers – no
head-tracking


Input Hardware
Tracker - Head
position and Orientation
- Determines viewpoint of
virtual world
- 5DT
3D-BIRD
- tracking of orientation angles
- move up, down, side to side, and rotate (yaw, pitch and roll)


Datagloves - Hand position and orientation
- Monitors
status of user's fingers
- 5DT
Data Glove 5 (www.5dt.com )
Measures each finger flexure and the orientation (pitch and roll) of the user's hand

Haptics - Force Feedback
- Phantom (http://www.sensable.com/ )
- 3 degrees of freedom
Other Input/Output Devices
Image Scanners
Printers (Raster)
Laser
Inkjet
Plotters (Vector)
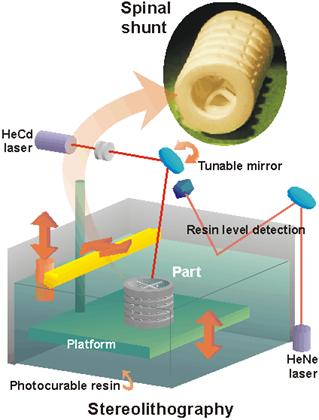
3D Printing
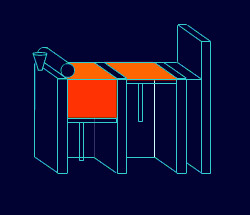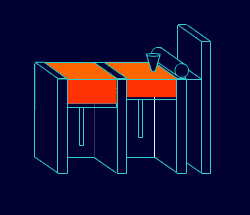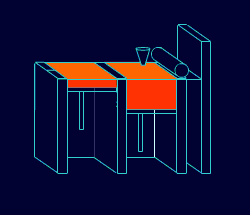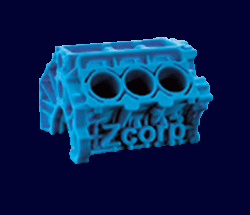
Stereolithography (from howstuffworks.com )
Create a 3-D model of object
Software slices model into thin layers -- typically five to 10 layers/millimeter
The 3-D printer's laser "paints" one of the layers, exposing the liquid plastic in the tank and hardening it
The platform drops down into the tank a fraction of a millimeter and the laser paints the next layer
This process repeats, layer by layer, until your model is complete

Ink-jet Printing – (e.g. Z-Corp )
- The 3D Printer spreads a thin layer of powder
- An ink-jet print head prints a binder in the cross-section of the part being created
- The build piston drops down, making room for the next layer, and the process is repeated
- Whenthe
part is finished, it is surrounded and supported by loose powder, which
is then shaken loose from the finished part.
Graphics Software
Languages -> Commands -> APIs
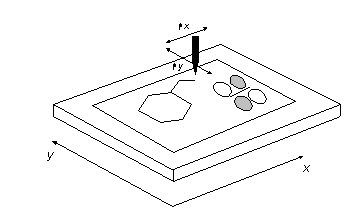
Coordinate Systems
Local Coordinates
World Coordinates
Device
Coordinates
Transformations
Model
-> World -> Normalized -> Device
Graphics
Functions
General
purpose graphics packages provide:
Functions
– I/O, attributes, transformations, viewing
Output
primitives – building blocks of images
Attributes
– properties of images
Geometric
transforms
Viewing
transforms
Software
Standards:
GKS
Phigs
OpenGL – http://www.opengl.org/
Web3D – www.web3d.org
