Computer Graphics |
|
GUIs |
What are Development tools? :
· Tools that help a developer convert interface specifications into an interactive system and that support all phases of system refinement including prototypes, implementation, testing, maintenance, and enhancement
Conventional Development Tools
Presentation stype enforcement - e.g. X, Mac, Win XP, Win3.1
e.g. X Windows:
Special client, called Window Manager, is responsible for overall look and feel
BUT:
Better - have toolkits, interface builders, user interface mgmt. Systems.
Toolkits - a variety of interface building blocks called widgets and language for putting together
e.g. Motif, Xview, Tk/Tcl , Java AWT (Swing), Python GUIs
· Widgets - buttons, menus, sliders, scrollbars, text editors, canvases for graphics, terminal windows
· Interfaces are built by using widgets, and programming languages (e.g Tk/Tcl)
· Widget Limitations:
o Widget sets are small and restrict interaction techniques
o Widgets are good for creating control panels BUT poor for what is seen inside. (e.g. Tk/Tcl for visualization resorts to OpenGL for graphics)
o Programming in an abstract language is not easy way for putting widgets together.
GTK (http://www.gtk.org/ )
· GTK+ is a multi-platform toolkit for creating graphical user interfaces.
· Offering a complete set of widgets
· GTK+ is suitable for projects ranging from small one-off projects to complete application suites.
GTK+ is based on three libraries developed by the GTK+ team:
The ATK library provides a set of interfaces for accessibility. By supporting the ATK interfaces, an application or toolkit can be used with such tools as screen readers, magnifiers, and alternative input devices.
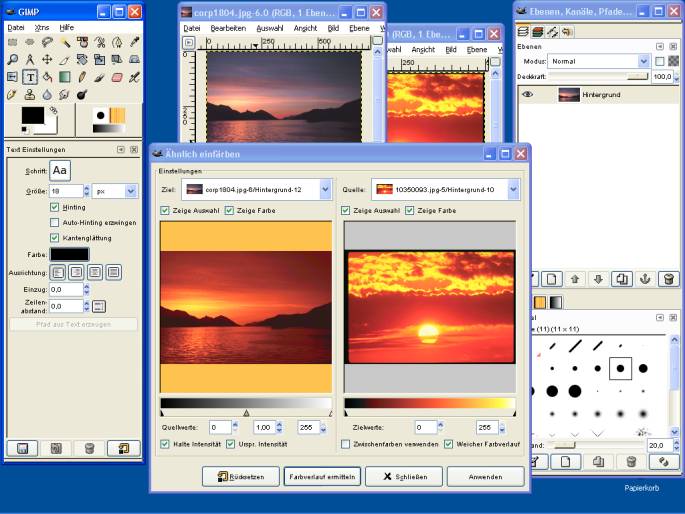
e.g. GIMP (http://www.gimp.org/ )
GIMP is the GNU Image Manipulation Program. It is a freely distributed piece of software for such tasks as photo retouching, image composition and image authoring. It works on many operating systems, in many languages.

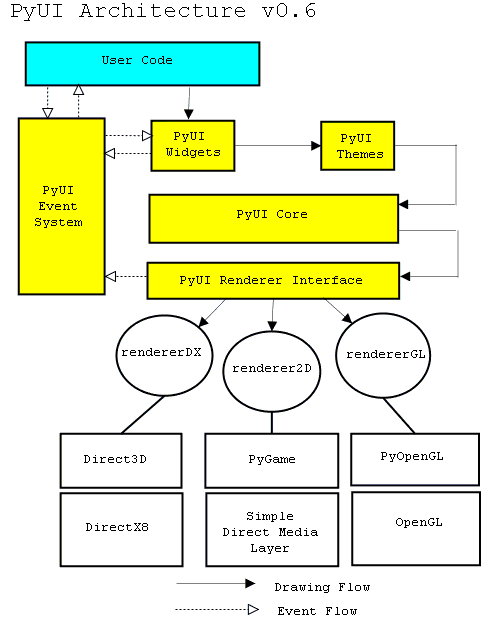
PyUI ( http://pyui.sourceforge.net/ )
PyUI is a user interface library written entirely in the high-level language python.
· Modular implementation that allows drawing and event input to be performed by pluggable "renderers".
o Makes PyUI very portable and scalable.
· Can run in environments from hardware accelerated 3D surfaces to regular desktop windows.
· PyUI was originally targeted as a User Interface for games, but it has evolved into a more general UI toolkit with applicability outside of games.
Features:
· A set of useful GUI widgets including buttons, list boxes, menus, and scrollbars
· Windows with resizability and movability
· An extensible event system for interacting with the user interface
· An interactive python console window
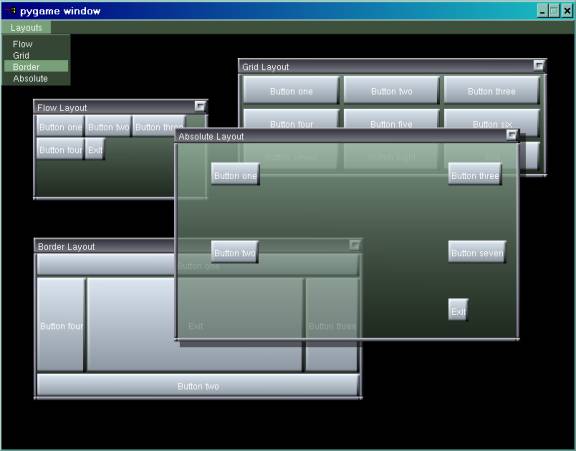
· Layout managers similar so the Java Swing layout managers
· Portability and scalability
Interactive Builders - provide a direct manipulation of graphical and interface toolkits. Some are integrated into toolkit environment, e.g.
Visual Gipsy for Tcl : http://www.prs.de/int/products/vg/index.html
Also can build interface prototypes with Macromedia Director and HyperCard
Examples:
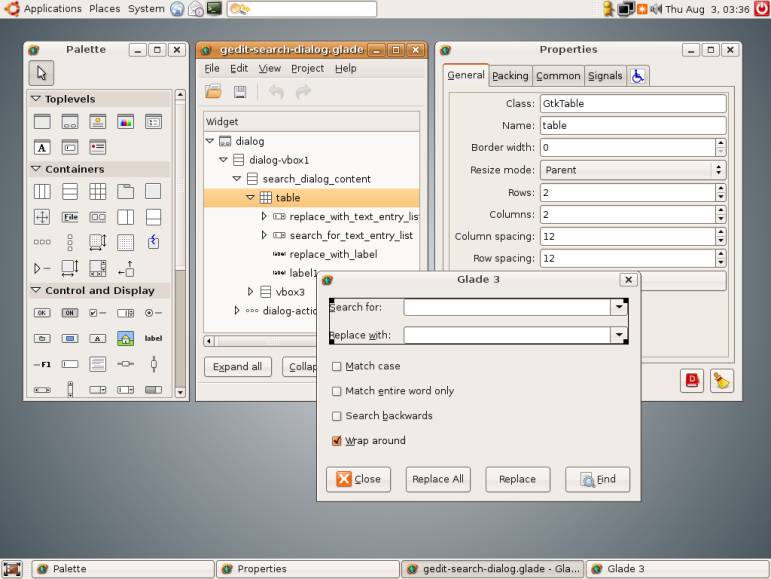
Swing Designer: http://www.swing-designer.com/
· Implements WYSIWYG GUI editing by dragging and dropping composites, layouts and controls.
· Implemented as a bi-directional tool - directly generates Java code which can be changed in the graphical editor or directly in source.
o All changes made directly to the source code will be reflected in the graphical designer.
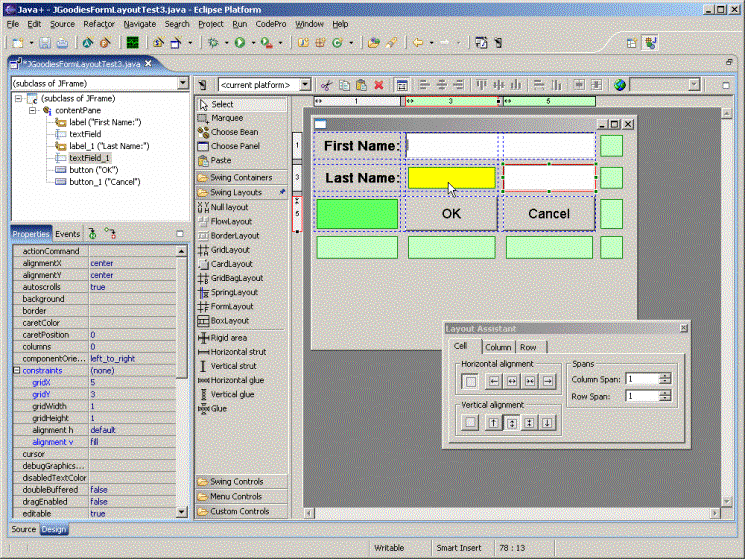
·NetBeans: http://www.netbeans.org/
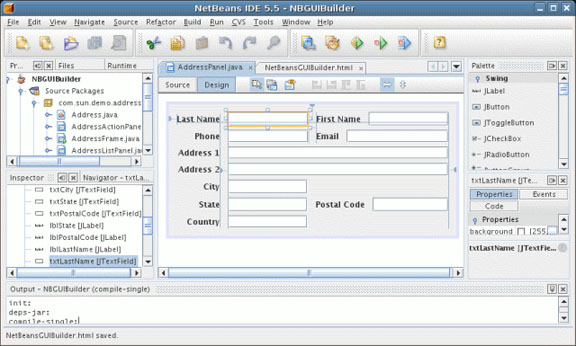
·
JFormDesigner: http://www.jformdesigner.com/
FormLayoutMaker: http://formlayoutmaker.sourceforge.net/
· FormLayoutMaker builds JGoodies Java forms
· JGoodies Forms ( http://www.jgoodies.com/freeware/forms/index.html ) framework helps layout and implement elegant Swing panels quickly and consistently
· FormLayoutMaker provides a WYSIWYG tool that enables developers to quickly layout Java screens using the JGoodies FormLayout layout manager.
· The result is an xml file containing all of the constraints.
Foam http://www.computersinmotion.com/
User
Interface Management Systems (UIMS) -
better said as "user interface development environments."
Separate
Applications into 3 modules:
Application Interface - how interface hooks into application code
Good -
Application and Interface separated
Bad
- Hard for designer to separate two
in practice
Novel Approaches to Developer tools
Garnet - System and Tools - comprehensive toolkit:
Examples of the interface are created and then the program is generated.
Sample Applications of Garnet:
http://www.cs.cmu.edu/afs/cs/project/garnet/www/screen-shots/screen-shots.html
Amulet - Garnet's Successor
http://www.cs.cmu.edu/afs/cs/project/amulet/www/amulet-home.html
User interface development environment for C++ and is portable across X11 on all kinds of Unix (Sun, Dec, HP, SGI, Linux, NetBSD, etc.), Microsoft Windows 95 and NT, and the Macintosh.
Amulet includes features designed to make creation of highly-interactive, graphical, direct manipulation user interfaces significantly easier employing:
full set of widgets.
Tools for Entire Development Cycle
Testing
Alternate Approach
- instead of "artifact centered"
of existing tools USE "semantically driven user interface
design."
Semantic model - interface developed as a declarative description and model becomes a plan that is used to let the developer manipulate in a way that is appropriate to its stage in the lifecycle.
e.g. IBM's Interactive Transaction System (ITS)
Style programs - implement actual widgets.
NOTE: Each layer corresponds to work roles of the development team members:
Graphic designers - compose style rules
Groupware
Toolkits
Supports
and augments group work where conventional toolkits do not work
e.g. Groupkit Project -
University of Calgary
http://www.cpsc.ucalgary.ca/grouplab/projects/GroupKit.html
Used for prototyping groupware, investigating multi-user architectures and interfaces, and as a CSCW teaching tool.
Example:
When one person presses the hello button, all people in the conference see that person say hello!
|
1.gk_initConf $argv
-command "gk_toAll
say_hi 6.pack .hello -side top
|
Example:
SharedNotes is a system that allows people to create and manipulate both personal and public notes between three devices: a personal digital, assistant (PDAs, in this case the Palm Pilot), a large public display, and their office computer (which acts both as a personal device and a system for remote collaboration).
Essentially, people can work on their PDAs or computers for personal work, bring some or all of their work into a meeting using a public display, work on the public display either directly or indirectly through their PDAs, and walk away with a record of all public contributions.
· DENIM is a system that helps web site designers in the early stages of design.
· DENIM supports sketching input, allows design at different refinement levels, and unifies the levels through zooming.
eg. http://dub.washington.edu/denim/denim_daily_files/page149.html
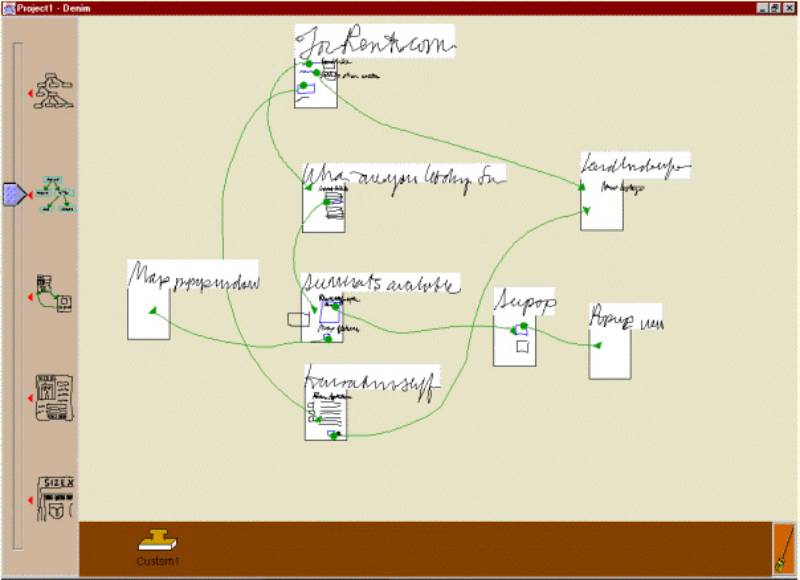
· Paper prototyping is a variation of usability testing where representative users perform realistic tasks by interacting with a paper version of the interface that is manipulated by a person ‘playing computer,’ who doesn’t explain how the interface is intended to work." – Paper Prototyping
· Paper prototyping can be used for virtually any type of human-computer interface – software, Web site, hand-held device, or even hardware.
· Its purpose is to get quick feedback from users while the design is still (literally) "on the drawing board."
· Some paper prototypes are hand-drawn, while others use printed-out screen shots.
http://www.paperprototyping.com/index.html - The Book
http://www.snyderconsulting.net/us-paper.pdf


Kit
http://www.infodesign.com.au/usabilityresources/design/paperprototypinggraphics.asp