|
SE 616 – Introduction to Software
Engineering |
|
Lecture 1 |
The Software Product
What is Software?
Software is a set of items or objects that form a "configuration" that includes
- programs
- documents
- data ...
Who Creates Software?
- Software
Engineers
Why is Software
Important?
- Affects
nearly every aspect of life.
How is Software Built?
By applying a structured process.
What are the Work Products?
- programs
- documents
- data
Dual Role of Software
- Product
- Process
that delivers products
Questions Asked of
Software Engineers
- Why does
it take so long to finish software?
- Why are
development costs so high?
- Why can’t we find all the bugs before delivery?
- Why do we
continue to have difficulties measuring progress in the software
development process?
Software Characteristics
- software
is engineered
- software doesn’t wear out
- software
is complex
- software
is like an ‘aging factory’
Software Custom Built
- Hardware
based on standards.
- Software
standard components exist.
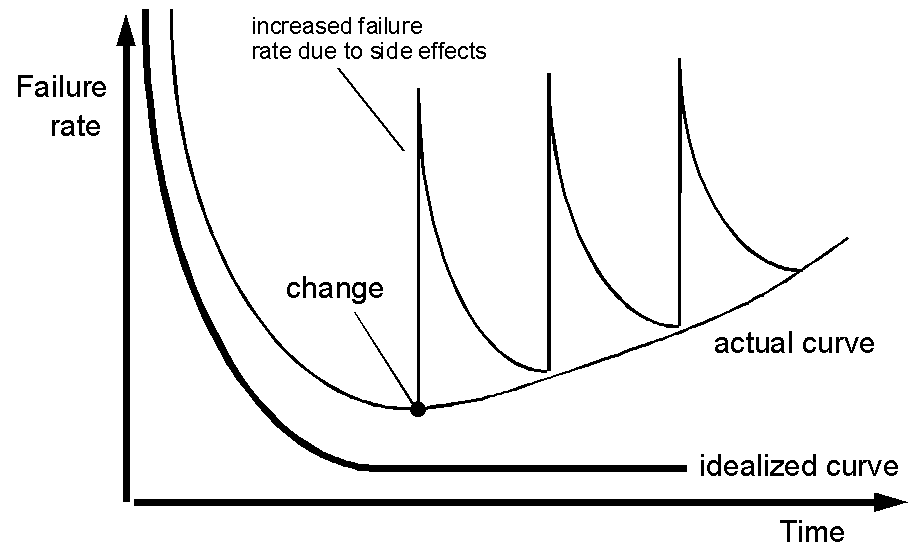
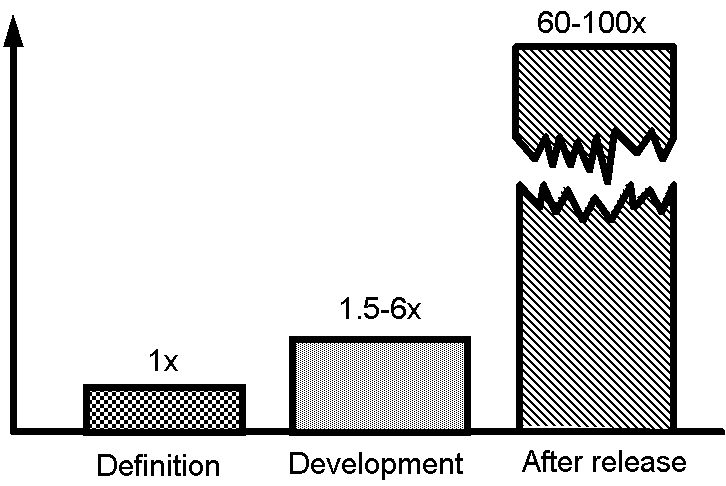
The Cost of Change
Software Applications
- system
software
- real-time
software
- business
software
- engineering/scientific
software
- embedded
software
- PC
software
- AI
software
- WebApps
(Web applications)
System Software
- Service
Programs – compilers, editors, OS’s, telecommunications
- Characteristics
--
- Heavy
interaction with hardware.
- Heavy
usage by multiple users.
- Concurrent
operation.
- Complex
data structures.
- Multiple
external interfaces.
Real-time Programs
- Monitors/analyzes/controls
real-world events
- Characteristics
--
- Data
gathering from external environments.
- Transformation
components.
- Control/output
components.
- Monitoring
components.
Business Software
- Discrete
systems (e.g. payroll, inventory, …)
- Management
and decision making.
- Interactive
computing.
Engineering and
Scientific Software
- Number
crunching.
- CAD.
- Simulation
/ Visualization
- Virtual
Reality
Embedded Software
- Resides in
ROM.
- System
Controllers.
PC Software
- Productivity.
- Graphics /
multimedia.
- Etc.
Web-based Software
- Browser-based
(CGI, HTML, Perl, Java, etc.)
AI Software
- Expert
Systems.
- Pattern
Recognition.
- Games.
Software Engineering
Challenges
- How do we
ensure the quality of the software we produce?
- How do we
meet growing demand and meet budget control?
- How do we
upgrade an aging software plant?
- How do we
avoid disastrous time delays?
- How do we
successfully institute new software technologies?
The Software Process
What is the software process?
- A series
of predictable steps.
Why is the software
process important?
- It
provides stability, control, and organization.
What are the steps in
the software process?
- Depends on
software to be developed.
What are the software
work products?
- Programs,
documents, and data.
How do I ensure that
the process is done correctly?
- Quality,
timeliness, long-term viability of products.
Software
Engineering Definition:
- The
establishment and use of sound engineering principles in order to
economically obtain software that is reliable and works efficiently on
real machines.
- (1)The
application of a systematic, disciplined, quantifiable approach to the
development, operation, and maintenance of software; that is, the
application of engineering to software. The study of approaches, as in
(1).
Process, Methods and
Tools.
- SE is a
layered technology.
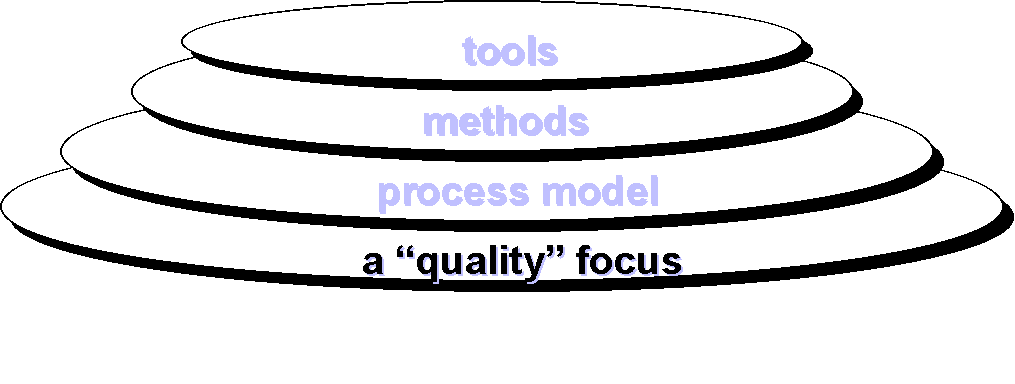
- SE
foundation – Process Layer
- Process
defines framework for set of Key Process Areas (KPAs) that are established
for delivery of SE technology.
- KPAs:
- foundation
for management control of products
- Set
context in which:
- Technical
methods are applied.
- Work
products produced.
- Milestones
established.
- Quality
assured.
- Change
managed.
Generic View of SE
- Engineering
is:
- Analysis
- Design
- Construction
- Verification
- Management
- Questions
to be answered:
- What is
the problem to be solved?
- What
characteristics of entity are used to solve problem?
- How will
entity and solution be realized?
- What
approaches will be used to uncover errors during design and construction?
- How will
entity be supported over long term?
SE: Three Generic
Phases
- Definition
Phase – What.
- What
information is processed.
- What
functions and performance are desired.
- What
system behavior is expected.
- What
interfaces are to be established.
- What
design constraints exists.
- What
validation criteria are required.
- Development
Phase – How
- How data
are to be structured.
- How
functions are to be implemented.
- How
procedural details are to be implemented.
- How
interfaces are characterized.
- How design
translates into programming language.
- How
testing will be performed.
- Support
Phase – Change
- Error
correction.
- Adaptation.
- Enhancements.
- Prevention.
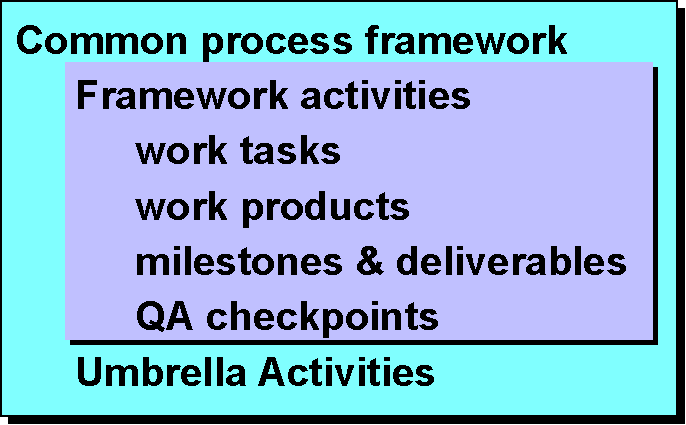
Umbrella Activities.
- Software
project management
- Formal
technical reviews
- Software
quality assurance
- Software
configuration management
- Document
preparation and production
- Reusability
management
- Measurement
- Risk
management
Software Process.
Common Process Framework
SEI Capability Maturity Model (CMM)
- Key
activities required at different levels of process maturity.
- Measure of
SE practice effectiveness.
- Five
process maturity levels (higher levels subsume lower):
- Level 1:
Initial – Ad hoc, few processes defined, success depends on
individual effort.
- Level 2:
Repeatable – Basic project management processes established to track
cost, schedule and functionality.
- Level 3:
Defined – Software process for management and engineering activities
are documented, standardized, and integrated into an organization-wide
software process.
- Level 4:
Managed – Detailed measures of software process and product quality
are collected.
- Level 5:
Optimizing – Continuous process improvement through quantitative
feedback from testing.
Key process areas (KPA) connected with each maturity level
(SEI).
- KPAs
define SE functions (e.g. plans, reviews) that must be present to satisfy
good practice at a particular level.
- KPA
characteristics:
- Goals
- Commitments
- Abilities
- Activities
- Methods
of monitoring
- Methods
of verifying
Software Process Models.
General Problem Solving Process
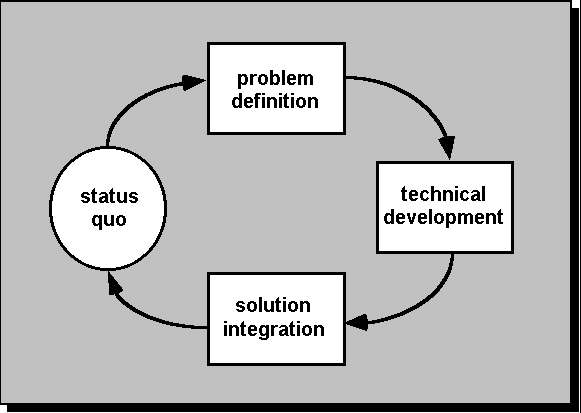
- General
Model Characteristic: Adaptable.
Framework activities will always be applied on every
project ... BUT the tasks (and degree of rigor) for each activity will vary
based on:
- The
type of project (an "entry point" to the model).
- Characteristics
of the project.
- Common
sense judgment; concurrence of the project team
Linear Sequential Model
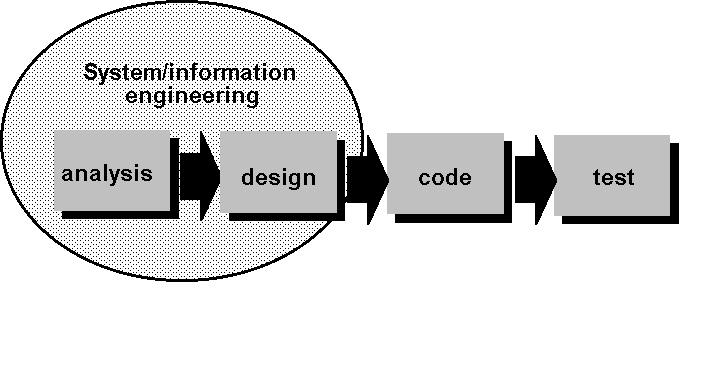
- Oldest
model – widely used.
- Problems:
- Real
projects rarely follow sequential flow.
- Often
difficult to specify all requirements explicitly.
- Long
process.
- Parallel
development slowed.
Prototyping Model
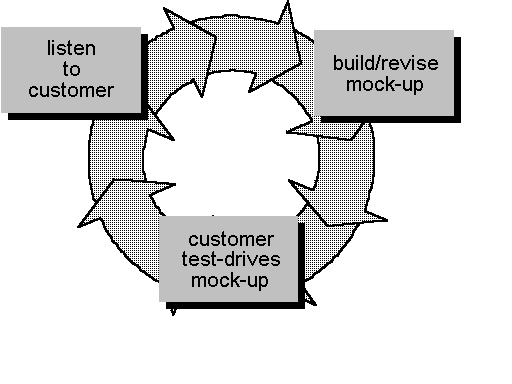
- Problems:
- First
System: Not usually written very well.
- Customer
thinks it is working version.
- Implementation
compromises made to build prototype.
- Usefulness:
- Good
communication tool.
- Fleshes
out system requirements.
RAD Model – Rapid Application Development
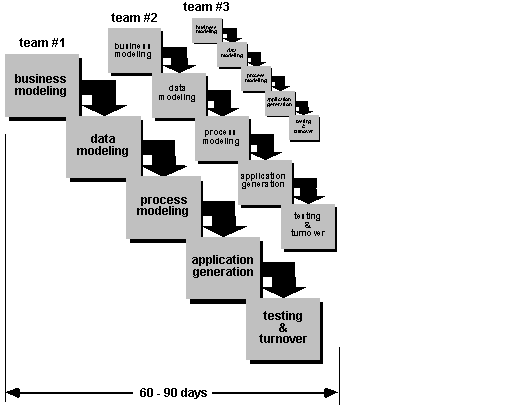
Characteristics:
- Iterative
model with short development time.
- High-speed
adaptation of linear model.
- Focuses on
building systems as collection of components.
- Phases:
- Business
Modeling
Information flow modeled: who, what, where info comes and
goes.
- Data
Modeling
Information transformed to data objects.
- Process
Modeling
Data objects transformed
- Application
Generation
4GL
methods used.
- Testing
and turnover
Reuses
modules.
Concerns:
- Large
projects require sufficient human resources.
- Requires
commitment of time by all.
- Does not
work with high-tech projects.
Incremental Model
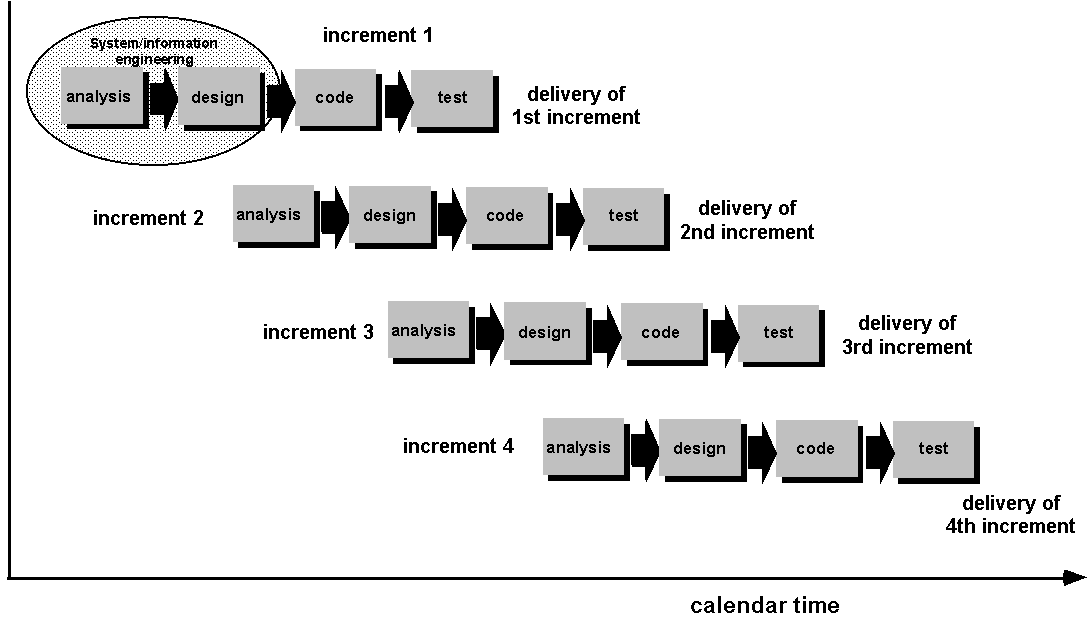
- Evolutionary
model
- Modified
linear model
- Each
sequence delivers an "increment" – 1st increment
core product, 2nd enhanced, etc.
- Intends to
deliver functioning product
Spiral Model
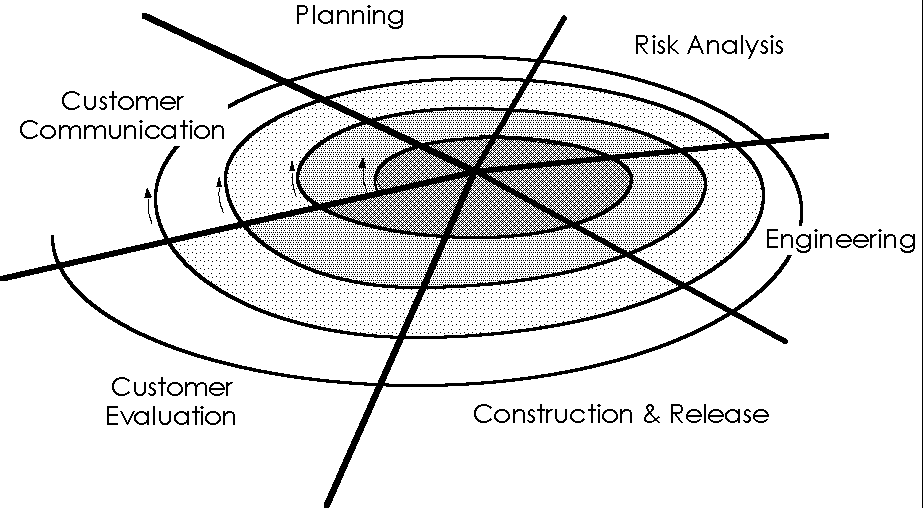
- Combines
concept of prototyping with linear model
- Process:
- Movement
counterclockwise from center.
- First
circuit: produces product specifications.
- Second
circuit: prototype.
- Third
circuit: refined versions.
- Each
pass through each regions produces adjusted
products.
- Adapted to
complete life cycle